
Archives
Wintermute CEO Denies Lawsuit Plans Against Binance
CEO Evgeny Gaevoy says market-maker Wintermute has no intention of suing Binance despite rumours linking them to the October 10 crypto crash.

Market-making firm Wintermute has officially denied widespread claims that it plans to sue Binance over losses incurred from the October 10 crypto-asset market crash. CEO Evgeny Gaevoy said his company ‘never had plans to sue Binance, nor see any reason to do it in future’, adding that rumours spreading online were based on insufficient facts.
literally nothing changed since this tweet and we never had plans to sue binance, nor see any reason to do it in future
I should probably ask to make a note of all the people spreading baseless rumors, but most of people believing these have goldfish memory capacity, so I wont https://t.co/0oHShby0Uk
— wishful_cynic (@EvgenyGaevoy) November 3, 2025
The statement follows speculation that Wintermute intended to seek recompense from Binance for alleged losses caused by a breakdown in a margin system. That incident, which led to the liquidation of more than $20 billion in leveraged crypto positions, triggered market uproar and prompted allegations of exchange liability.
Rumors, Response, and Clarification
Wintermute, which provides liquidity on major cryptocurrency platforms including Binance, was named by social-media accounts as a potential claimant in legal action. A prominent user claimed Wintermute had transferred over $700 million into a Binance wallet shortly before the market crash and planned to file suit. Gaevoy dismissed these allegations as ‘complete bullshit’, emphasising that no formal damages claim or legal filing has been initiated.
Binance’s then-CEO responded to the situation by advising followers to rely on verified information rather than unconfirmed social-media posts. The exchange said it did not recognise any legal demand from Wintermute and declined to comment on individual firm positions. The market maker’s denial aims to restore clarity amid persistent rumours, uncertainty and trading-volume disruption following the crash.
Industry Response and Forward View
The episode highlights the fragile intersection between decentralised trading firms, centralized exchanges and the legal environment in crypto markets. For liquidity providers and exchanges, the dispute underscores how quickly operational incidents can evolve into accusations of structural failure, even if no formal legal action is taken.
Observers should monitor how Wintermute and other market-makers adjust their risk-management and exchange-relationship frameworks. Key indicators include whether any litigation is filed, how other exchanges respond to liability questions, and how transparency improves around exchange auto-deleverage systems. Although the immediate legal temptarion appears defused, the broader question remains: how will firms govern exposure and accountability in volatile crypto events?
The October crash marked a tremor in the crypto ecosystem not just for prices, but for how infrastructure participants evaluate counter-party risk and operational resilience. Wintermute’s clarification may serve as a stabilising message, but the incident’s after-effects may continue shaping market behaviour.





France Approves 1% Tax on ‘Unproductive’ Wealth, Including Crypto Assets
French MPs passed a measure to levy a 1% tax on so-called ‘unproductive wealth’ over €2 million, extending the tax base to include cryptocurrencies and luxury assets.

France’s National Assembly has voted to introduce a new 1% annual tax on ‘unproductive wealth’ for individuals with total assets exceeding €2 million. The measure redefines the country’s existing property wealth tax, expanding it to include cryptocurrencies, art, yachts, private jets, and other non-productive holdings that previously escaped taxation.
Lawmakers said the reform aims to rebalance the French tax system by targeting idle wealth rather than assets that contribute directly to the economy. Properties rented long-term or used for business activity remain exempt. However, high-value personal assets and digital tokens now fall within the scope of the new levy.
Purpose and Economic Rationale
The tax overhaul marks France’s most significant shift in wealth policy in recent years. By labeling digital and luxury assets as ‘unproductive’ the government seeks to encourage investment in businesses, real estate, and job creation rather than passive wealth storage. Officials project the change could generate up to €2 billion annually in new revenue.
Crypto assets are a key focus of the reform. Policymakers view large-scale crypto holdings as both a source of inequality and a potential threat to financial transparency. The new law ensures that even unrealized digital-asset holdings are taxed as part of total wealth, not just when profits are realized.
Supporters of the measure argue it will redirect capital toward more productive sectors and close long-standing tax loopholes. Critics, however, warn that the flat 1% rate may penalize mid-level millionaires and drive wealthy individuals to relocate their assets abroad.
Market Reactions and Future Implications
For investors and crypto holders in France, the reform raises new challenges in valuation, reporting, and asset planning. Authorities will now require comprehensive declarations of digital wallets and high-value collections, making crypto wealth a visible part of the national tax base.
Analysts say the move could inspire similar actions across Europe, where governments are seeking to adapt tax frameworks to a digital economy. The success of France’s approach will depend on enforcement efficiency and whether it sparks new tax migration among the wealthy.
The boundary between finance and digital assets continues to blur and France’s new wealth tax signals that governments are increasingly treating crypto holdings as tangible economic assets rather than speculative instruments.




AI Startup Mercor’s 22-Year-Old Founders Become World’s Youngest Self-Made Billionaires
Three 22-year-olds behind AI recruiting startup Mercor have become the youngest self-made billionaires after the company raised $350 million at a $10 billion valuation.

Three entrepreneurial 22-year-olds – Brendan Foody (CEO), Adarsh Hiremath (CTO) and Surya Midha (Board Chairman) – have become the world’s youngest self-made billionaires following a major funding round that valued their San Francisco-based AI recruiting startup, Mercor, at approximately $10 billion. The company secured $350 million in fresh investment, fueling its climb to the top of the wealth charts and surpassing the previous youngest-founder record.
Founded in 2023, Mercor specializes in matching skilled contractors—including PhDs, software engineers and lawyers with leading AI labs that require human-in-the-loop support for model training, data annotation and short-term AI-development tasks. The platform currently engages more than 30,000 contractors globally, paying out over $1.5 million per day to support its rapid growth and high-demand operations.
Startup Success in the AI Talent Economy
Mercor’s success reflects a surge of demand for human talent to train and refine artificial-intelligence models jobs that are often overlooked but essential. The company’s platform manages large-scale sprints of human judgment and niche skillsets, tapping into a labour category that intersects software, law, data science and content moderation. By positioning itself at this intersection, Mercor gained traction with major AI labs and venture-capital firms alike.
The co-founders’ unconventional path also stands out. Hiremath and Midha both left Ivy League institutions – Harvard and Georgetown respectively – while Foody departed his economics studies to focus on building the business full-time. Their early decision to turn down traditional career tracks and scale a venture at 18-20 years old became a critical factor in their fast ascent.
Beyond the founders’ personal journey, Mercor’s expansion shows how the AI-economy is no longer just about algorithms – it’s about the human input behind them. The company’s growth signals that the “talent pipeline” for AI is itself a major startup opportunity, with funding and valuations reflecting that shift.
Startup Trends and Future Challenges
For the broader startup ecosystem, Mercor’s achievement raises several signals. First, AI-adjacent businesses beyond model architecture, such as training data, human workflows and platform orchestration – are attracting high valuations. Second, youth entrepreneur stories are once again capturing investor imagination, especially in next-wave tech sectors.
However, executing at scale remains a challenge. Promising growth depends on maintaining service quality, managing global labour compliance, core-team retention and staying ahead of automation, which may eventually reduce the need for large human pools. Investors and industry watchers will track whether Mercor can extend its model beyond labour-sourcing into adjacent AI-service verticals and whether it can defend its valuation in an economy that is already recalibrating AI’s real-world returns.





Romania Blacklists Polymarket Over $600M Crypto-Betting Surge
Romania’s gambling regulator has added Polymarket to its blacklist, citing more than $600 million in crypto-event wagers during recent elections and declaring the platform an unlicensed gambling operator.

Romania’s gambling regulator, the National Office for Gambling (ONJN), has officially blacklisted Polymarket, describing the prediction-market platform as an unlicensed gambling operator. The move follows the regulator’s findings that Polymarket-enabled event trading generated trading volumes exceeding $600 million during the country’s recent presidential and local-government elections.
Under national legislation, the ONJN said Polymarket’s “counter-party betting” model – where users wager directly against one another on future outcomes – qualifies as gambling regardless of whether the bets are denominated in fiat or crypto. As a result, internet service providers in Romania are now required to block access to the platform.
Regulatory Push and Enforcement Context
The ONJN emphasised that its decision is motivated by legal obligations, not the underlying technology. “Whether you bet in lei or crypto, it must be licensed,” said ONJN President Vlad‑Cristian Soare. The regulator highlighted several breaches, including a lack of fiscal reporting, inadequate anti-money-laundering controls and the absence of player-protection mechanisms standard requirements under Romania’s gambling framework.
Polymarket has faced similar scrutiny in other jurisdictions. Authorities in Belgium, France, Poland, Singapore and Thailand have also restricted the platform, while the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission previously fined the company for operating unregistered derivative markets. The escalating global regulatory focus signifies growing tension between innovative crypto-asset services and existing gambling and financial laws.
Industry Implications and Market Signals
For the broader sector of crypto-enabled prediction markets, Romania’s action is a critical signal. It underlines that despite decentralised architectures, platforms which facilitate outcome-based wagers may be treated as gambling under national law with or without crypto involvement. Operators in this space must now anticipate regulatory enforcement across multiple markets and plan for access restrictions or structural adjustments.
Investors and users should watch for three key signals: how Polymarket responds in terms of licensing or product redesign; whether other national regulators follow Romania’s lead; and how ancillary markets, such as sports or economic-event trading adjust to tightened oversight. As previously covered, the shift from experimental blockchain services to regulated financial environments is occurring rapidly. Romania’s blacklisting of Polymarket may mark a turning point for how event-trading platforms align with traditional compliance regimes.




Berkshire Hathaway Cash Pile Hits Record $381.7B as Earnings Surge 34%
Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway reported record cash holdings of $381.7 billion and a 34% jump in operating earnings, driven by strong insurance results and restrained disaster losses.

Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway reported another strong quarter, posting record cash reserves of $381.7 billion and a sharp increase in operating earnings. The figures underscore the conglomerate’s ability to generate profit even as it maintains a conservative stance toward new acquisitions in a high-rate environment.
Operating earnings rose 34% year over year to $13.5 billion, compared with $10.1 billion a year earlier. The surge was driven primarily by a tripling in insurance underwriting profit, thanks to exceptionally low disaster-related claims during the quarter.
Net income – which includes both operational performance and investment results – climbed 17% to $30.8 billion, up from $26.3 billion in the same period last year. Despite the record profit, Berkshire did not repurchase its own shares in the quarter, signaling that Buffett still views the stock as fully valued in the current market.
Inside Berkshire’s Record Quarter
The company’s investment portfolio grew to $283.2 billion from $257.5 billion in the previous quarter. Nearly two-thirds of Berkshire’s holdings are concentrated in five major U.S. companies: Apple, American Express, Bank of America, Coca-Cola, and Chevron.
Insurance remained the standout performer, while the railroad, utilities, and energy divisions delivered steady – though more modest – gains. The strength in insurance underwriting offset weaker results in some industrial holdings, helping Berkshire post one of its strongest quarters in recent years.
Buffett’s strategy of stockpiling cash and limiting major acquisitions continued to pay off. By the end of the quarter, the company’s cash balance had risen from $344 billion in the second quarter to $381.7 billion, marking the highest level in its history.
Investor Outlook and Market Implications
Analysts say Berkshire’s record liquidity positions it as both a stabilizer and an opportunistic buyer if market conditions shift. With interest rates still elevated, Buffett’s cautious approach allows the firm to earn meaningful returns on short-term Treasury holdings while keeping capital ready for future deals.
The company’s rising profits also highlight the resilience of its core businesses, particularly insurance, which has benefited from disciplined underwriting and higher investment income.
However, Buffett has repeatedly warned that attractive acquisition targets are scarce, suggesting Berkshire’s massive cash position may remain untouched unless valuations decline. For investors, the quarter reinforces Berkshire’s reputation as a defensive powerhouse – capable of outperforming through cycles while waiting for the next major opportunity.





Elon Musk Unveils X Chat: Messaging App With Bitcoin-Style Encryption
Elon Musk announced a new messaging app, X Chat, featuring peer-to-peer encryption ‘kind of like Bitcoin’ and designed to rival WhatsApp with privacy-first architecture.

Elon Musk revealed plans for a new messaging application named X Chat, built on his platform X and expected to launch independently in the coming months. The app features a peer-to-peer encryption system that Musk described as “kind of like Bitcoin,” and is built to support secure texting, file sharing, and audio/video calls without the advertising infrastructure common in competing services.
Architecture and Strategy Unpacked
Musk said that X Chat represents a complete rebuild of X’s direct-messaging stack, now engineered for privacy and decentralised communication. He noted that unlike rivals such as WhatsApp, the app will strip out the traditional “hook” for ad targeting, arguing that such hooks are security vulnerabilities. The new encryption model is designed to avoid the collection of metadata and tracking, aligning more closely with how blockchain ecosystems protect value and identity.
By framing the encryption layer as “Bitcoin-style,” Musk highlighted the peer-to-peer architecture – users connect directly rather than through centralised servers. The app is expected to debut first within the X ecosystem and later as a standalone download, signalling Musk’s ambition to turn X into a multifunctional platform with messaging as one pillar of an “everything app” strategy.
Market and Industry Implications
For the tech and communications industries, X Chat brings a new entrant into the highly competitive encrypted-messaging market. The privacy upgrade positions X against apps with significant user bases, such as WhatsApp, which is part of Meta and signals that messaging platforms are racing to offer deeper security. If executed properly, X Chat could challenge incumbents by appealing to users dissatisfied with ad-driven models or metadata collection.
However, the road ahead is not without challenges. User adoption will depend on trust in the encryption design, the ability to attract contacts and integrate mainstream features like group chats and calls. Regulatory oversight is another concern given global scrutiny of encrypted communication. Key indicators to watch include the launch timing, supported features, encryption protocol transparency and whether X-Chat’s usage metrics grow independently of X’s social network traffic. As previously covered, the shift toward privacy-centric messaging reflects a broader demand for data self-sovereignty and X Chat may become a test case for how that demand scales.





Bill Gates Predicts AI Will Cut Workweek to Two Days
Bill Gates says artificial intelligence could replace most jobs within a decade, leading to a two-day workweek and forcing society to rethink the role of human labor.

Billionaire philanthropist and Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates says artificial intelligence could fundamentally reshape the global workforce, reducing the standard workweek to just two days within the next decade. Speaking at recent public appearances, Gates described AI’s rapid progress as both “profound and unsettling,” predicting it will replace humans in most routine and complex jobs.
He said the next technological era, which he calls one of “free intelligence,” could solve widespread shortages in sectors like healthcare and education but would also raise deep questions about how people spend their time and what roles remain distinctly human.
“It’s kind of profound because it solves all these specific problems – like we don’t have enough doctors or mental health professionals, but it brings with it so much change,” Gates said. “What will jobs be like? Should we just work two or three days per week?”
The Future of Work in an AI Economy
Gates envisions a world where artificial intelligence handles most production, logistics, and service tasks. In that scenario, humans might focus on creativity, leisure, and social interaction rather than traditional labor. “We’ll decide, like baseball – we won’t want to watch computers play baseball, so there will be things we reserve for ourselves” – he said.
While Gates framed the transition as inevitable, he acknowledged uncertainty over how governments, economies, and individuals will adapt. “It’s very profound and even a little bit scary, because it’s happening very quickly, and there’s no upper bound” – he said.
Companies experimenting with shorter workweeks are already seeing benefits. U.S. – based firm Exos reported a 24% boost in productivity and a 50% drop in burnout after shifting to a four-day schedule. In Japan, Tokyo introduced a four-day workweek for government employees to improve work-life balance and address overwork-related health issues.
Innovation, Inequality, and the Human Question
Not everyone views the AI revolution optimistically. AI pioneer Geoffrey Hinton, often called the “Godfather of AI,” has warned that unchecked automation could dramatically widen the wealth gap. He argues that while AI may boost global productivity, profits could disproportionately flow to corporations and the wealthy, leaving displaced workers behind.
“We’re talking about a huge increase in productivity,” Hinton said in a recent discussion. “Everybody ought to be better off, but actually it’s going to be the other way around.” He cautioned that growing inequality could create “fertile ground for extremism.”
Gates agrees that society must prepare for those challenges. While he celebrates AI’s potential to spark innovation, he emphasizes that technology alone cannot determine whether the coming changes improve human life. “It’ll take time, but I think we can shape it if we start now” – he said.
AI’s rise is redefining work, wealth, and purpose and the question may no longer be whether machines can replace human labor, but how humans choose to adapt once they do.





BofA Sees Gold & China Stocks as Smart Hedges in AI Boom
Bank of America strategist Michael Hartnett says gold and Chinese equities offer the strongest protection for investors riding the artificial-intelligence boom.

Bank of America’s lead investment strategist, Michael Hartnett, has highlighted gold and Chinese stocks as the best hedges for investors navigating the current artificial-intelligence-driven equity market. Hartnett points to valuations stretched in the U.S. tech sector and growing exposure to AI themes as reasons to diversify with non-traditional assets that may fare better if sentiment turns.
Valuation Alert and Hedge Strategy
Hartnett argues that while U.S. mega-cap tech companies continue to draw money amid AI enthusiasm, the risk of a sharp correction is rising as investor breadth narrows and valuations expand. He notes that gold has historically performed well when speculative equity markets become overheated. Chinese stocks, by contrast, offer undervaluation and regional-specific exposure outside U.S. tech dominance. Importantly, both gold and China equities provide diversification away from the richest parts of the market, making them complementary rather than competing positions.
He emphasises that investors should view hedges not as protective anchors alone but as active parts of a portfolio that can perform in alternative scenariosб such as a tech bubble deflating or global growth stalling.
Portfolio Insights and Market Signals
For investors, Hartnett’s take signals a thematic shift: successful portfolios may require more than owning the hottest tech names. Allocations to gold – driven by safe-haven demand and Chinese equities – backed by regional rebound potential – could help cushion volatility and structural risk. The performance of gold and China stocks may also amplify if U.S. tech falters or AI growth disappoints. Key signals to monitor include inflows into gold-backed funds, ETF flows into Chinese equities, changes in Chinese regulatory policy and any signs that U.S. tech breadth is weakening.
The broader implication is that the AI-fuelled rally may be entering a phase where hedging matters more than chasing excess returns. Investors increasingly need to ask: what happens if the AI story slows, valuations compress or global growth slips? In that light, Hartnett’s message acts as a reminder that owning the trend is rarely enough -preparing for what happens when it changes is equally important.





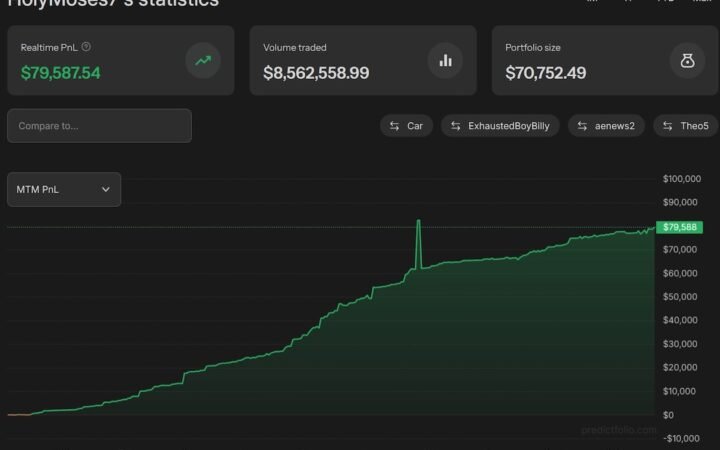
Polymarket Trader Turns $1 Into $80,000 Through Election Bets
A Polymarket user has reportedly grown a $1 balance into over $80,000 in one year by trading political and event-driven markets, showcasing the rising appeal of prediction markets.
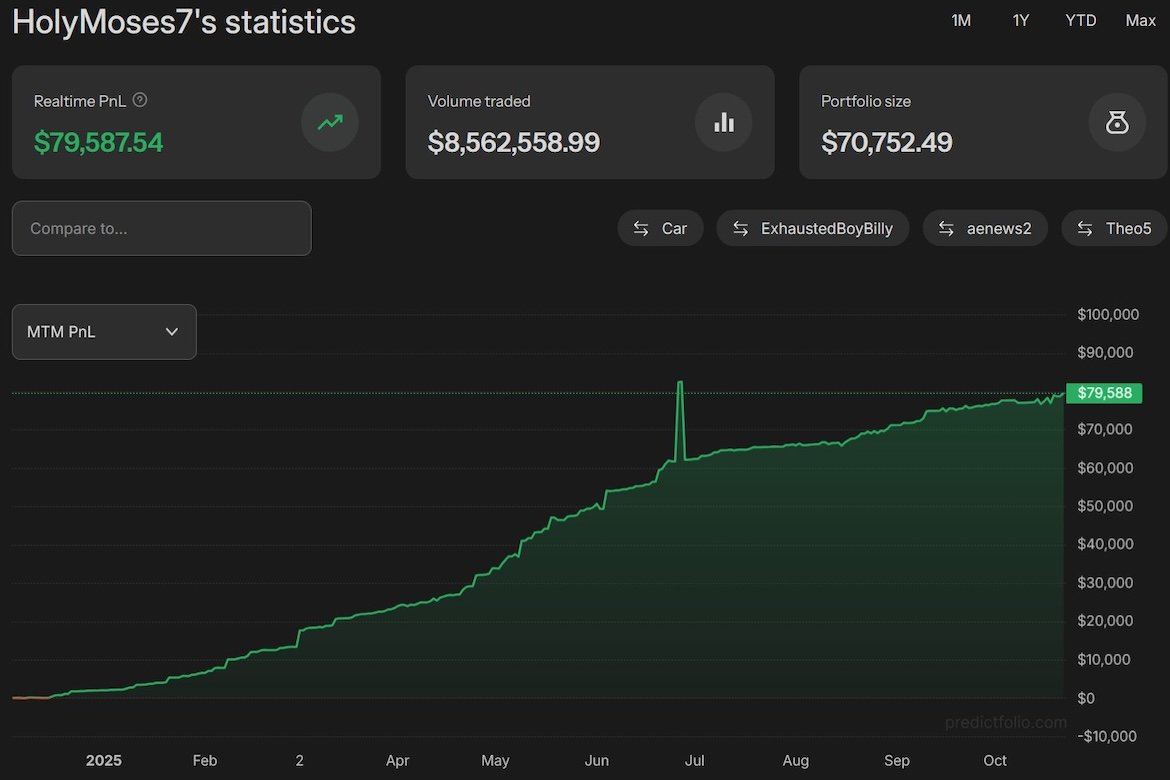
A retail trader active on the blockchain-based prediction platform Polymarket says they have turned an initial $1 investment into more than $80,000 in just one year. Posting under the handle Holy Moses, the trader shared their results and strategy, outlining how a mix of focus, volatility, and persistence transformed a small test wager into a full-scale trading operation.
From $1 to over $80k in a year. This is my @Polymarket journey.
My journey in started a couple of days prior to US elections with a single dollar. I focused on volatile polymarkets including the Balance of Power and Trump rallies which had tons of liquidity and volume. In a few… pic.twitter.com/uLjfPNAZ6P
— Moses (@holy_moses7) October 22, 2025
According to the trader, their journey began just before the U.S. elections, starting with modest bets on high-liquidity markets such as Balance of Power outcomes and Trump rally participation. Within days of the election, those positions had multiplied several hundredfold as trading activity surged.
Inside the Strategy
The trader explained that they focused on high-volume, fast-moving markets where liquidity enabled active speculation and short-term exits. Their approach evolved to include global elections, geopolitical outcomes, and even pop-culture topics like the frequency of Elon Musk’s social media posts.
Over time, the trader reported monthly profits averaging between $6,000 and $7,000, with the majority of gains coming from election-based markets. According to their own remarks, the key to success was combining event research, sentiment tracking, and risk control rather than relying on chance.
They described the path as “the road from $1 to $1 million,” acknowledging that while the goal remains aspirational, consistent discipline and market understanding make it feasible. “It’ll take time, but I’m persistent,” the trader noted.
Prediction Markets and Industry Impact
Polymarket, a blockchain-powered prediction platform, has grown rapidly over the past year, with users speculating on everything from global politics to macroeconomic trends. The platform’s popularity illustrates how decentralized prediction markets are becoming a new frontier for data-based speculation, enabling retail traders to profit from real-world events.
However, the rise of event markets also highlights broader debates over regulation, transparency, and market integrity. Analysts caution that while outsized returns are possible, most users face steep learning curves and volatility risks.
Prediction markets sit at the crossroads of finance, gaming, and analytics – blending probability trading with crowd forecasting. Stories like this one underline both their profit potential and inherent risk, showing how innovation continues to blur the line between investing and speculation.





Revolut Lets Users Swap U.S. Dollars for Stablecoins at 1:1 Rate
Fintech firm Revolut is offering U.S. dollar customers the option to swap fiat into major stablecoins at a one-to-one rate, signalling deeper integration of digital assets in everyday finance.

Fintech company Revolut has introduced a new offering that allows users to convert U.S. dollars into selected stablecoins at a fixed one-to-one rate, without fees or spreads. The service supports stablecoins such as USDC and USDT across several major blockchain networks, providing users a seamless route from fiat to digital assets.
Bridging Traditional Finance and Crypto
The move marks a shift in how digital banking platforms connect traditional currency with tokenised assets. By removing conversion costs and setting a one-to-one rate, Revolut lowers the friction for users looking to access stablecoins assets increasingly used for payments, trading and global finance. The feature also reflects regulatory maturity, as Revolut recently secured crypto-asset licensing in European markets and pivots towards regulated digital-asset services.
The integration across multiple blockchains addresses operational bottlenecks: users can choose networks familiar to them and avoid manual bridging between chains. For Revolut’s wider user base spanning tens of millions globally – the swap feature enhances on-ramp capability and positions the platform as a bridge between fiat banking and crypto ecosystems.
Long-Term Impact and Opportunities
From an investment and user-perspective, the swap service expands access to stablecoins and may accelerate inflows into digital-asset ecosystems. This could also support global transfers, corporates leveraging stablecoins for payments and retail users shifting portions of their savings into digital formats. Yet, risks remain. Stablecoins depend on the credibility of their issuers, regulatory frameworks are still evolving and network-choice can affect costs and settlement times.
Users should monitor which stablecoins gain adoption via Revolut, whether usage extends beyond trading into payments or savings, and how regulators respond to fiat-to-token conversions in different jurisdictions. As previously covered, the convergence of digital banking and crypto indicates that stablecoins are becoming a mainstream feature – not just niche investments.





Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan Sees $1 Trillion Market for Solana
Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan outlined a bullish thesis for Solana (SOL), arguing it can mirror Bitcoin’s early dominance by tapping tokenisation and stable-coin growth.

Bitwise chief investment officer Matt Hougan presented a detailed framework for why Solana may be the most compelling blockchain investment today. He argues the asset offers “two ways to win”: capturing growth in the stable-coin and tokenised-asset market and increasing its share of that rapidly expanding pool. He estimated the combined market for tokenisation and stable-coins at around $768 billion- of which Solana currently holds about 14%, placing its valuation near $107 billion.
1/ The best crypto investments give you two ways to win. A thread exploring one reason I’m so bullish on Solana.
🧵
— Matt Hougan (@Matt_Hougan) October 30, 2025
Solana’s Growth Case Explained
Hougan draws parallels with Bitcoin’s trajectory, where investors benefited both from deepening adoption of the store-of-value market and Bitcoin’s rising share within it. He sees Solana playing a similar game: growth in tokenised finance and securing share among Layer-1 blockchains. He cites Solana’s technical strengths- high throughput, low latency and vibrant developer ecosystem – as core advantages over more established rivals like Ethereum. He also pointed to real-world traction, noting that institutional brands are already building on Solana, which supports his conviction that the asset is positioned well to benefit if the market grows ten-fold from current levels.
Investor Outlook and Long-Term Potential
For investors, Hougan’s approach signals a shift: rather than betting solely on a blockchain’s size today, the focus is on structural growth and relative share gain. If Solana succeeds in both arenas, the upside could be significant. Yet execution risk looms large. The blockchain must convert infrastructure credibility into institutional flows, maintain token-economics durability and navigate regulatory scrutiny around staking and token-based products. Indicators to watch include future ETF launches linked to Solana, institutional wallet inflows, token-staking uptake and competitive positioning versus other chains. As previously covered, tokenised infrastructure is moving from speculative to foundational Solana’s next phase may determine whether it becomes a dominant network or a tactical challenger.




‘Big Short’ Investor Michael Burry Warns of Market Bubble
Michael Burry, famed for predicting the 2008 crash, has broken nearly two years of silence to warn that markets may be in a bubble and that ‘sometimes the only winning move is not to play’.

Michael Burry, the legendary hedge-fund manager best known for foreseeing the 2008 housing collapse, has resurfaced after almost two years away from public commentary. In a brief statement shared on social media, he cautioned that “sometimes, the only winning move is not to play,” a line interpreted as a warning about what he sees as excessive speculation across financial markets.
Sometimes, we see bubbles.
Sometimes, there is something to do about it.
Sometimes, the only winning move is not to play. pic.twitter.com/xNBSvjGgvs— Cassandra Unchained (@michaeljburry) October 31, 2025
His comment arrives as U.S. equities hover near record highs, driven largely by a handful of technology giants. Despite those gains, many analysts note that participation has narrowed and that smaller companies remain under pressure. Against this backdrop, Burry’s words resonate as a reminder of the risks that come with concentrated market enthusiasm and stretched valuations.
Burry’s Caution in Context
Burry’s record lends his caution particular weight. His prescient call on the 2008 subprime-mortgage collapse made him one of the most influential contrarian voices in modern finance. This time, his warning appears to focus on the imbalance between rising stock prices and slowing economic momentum. With growth moderating, rates still elevated, and liquidity tightening, he seems to suggest that risk assets may no longer offer adequate compensation for potential downside.
The message also points to a deeper critique of investor psychology. In an era dominated by momentum trading, passive index flows, and speculative optimism, Burry’s advice to “not play” can be read as a call for restraint a reminder that avoiding losses can sometimes be the most effective strategy when fundamentals and valuations diverge too widely.
Market Reaction and Future Risks
Burry’s remarks add to a growing chorus of concern among market veterans who see warning signs in the current cycle. Equity valuations remain elevated, volatility has returned, and sentiment surveys show investors increasingly polarized between fear of missing out and fear of correction.
For now, markets continue to ride optimism around corporate earnings and artificial-intelligence growth, but his intervention may prompt some to rethink risk exposure. The coming months will test whether the rally can broaden beyond mega-cap tech or whether it succumbs to fatigue after such a long advance.
As previously covered, every bull market carries echoes of past cycles and Burry’s return to the conversation suggests that even the most confident investors should remember how quickly euphoria can shift to caution.





Which Serves as the Better US Dollar Hedge Gold or Bitcoin?
Gold has surged over 50% this year, while Bitcoin is up about 13%, raising questions about which asset truly functions as a hedge against a weakening US dollar.

Gold and Bitcoin are both widely viewed as alternatives to the US dollar – potential shelters from inflation or currency debasement. Yet in 2025, their performance has sharply diverged. Gold has climbed more than 50%, while Bitcoin has gained only 13%, modestly trailing the S&P 500.
This divergence raises questions about the assumption that both assets serve the same function. Over recent trading periods, the two have often moved in opposite directions- when gold fell, Bitcoin rallied, and vice versa. Such behavior challenges the idea that they represent interchangeable dollar hedges.
Why Their Paths Diverge
Several key dynamics explain why gold and Bitcoin are moving out of sync:
- Different investor bases: Gold is held by central banks and institutions as a long-term store of value, while Bitcoin’s ownership skews toward retail traders and speculative investors.
- Market sensitivity: Gold typically rallies in periods of economic stress, inflation, or geopolitical tension. Bitcoin, by contrast, tends to rise during risk-on periods tied to tech optimism or liquidity surges.
- Volatility and history: Gold’s multi-century track record contrasts with Bitcoin’s shorter and far more volatile performance history. The latter behaves more like a high-growth asset than a stable hedge.
- Capital rotation: Rather than investors moving into both simultaneously, capital often shifts between the two depending on macro conditions, risk sentiment, and liquidity.
Together, these factors reveal that gold’s rally this year reflects safe-haven demand, while Bitcoin’s smaller gain mirrors its closer ties to speculative risk appetite.
Portfolio Strategy and Key Takeaways
For investors deciding between gold and Bitcoin as a dollar hedge, several takeaways stand out:
- Gold remains the traditional hedge – its stability, institutional ownership, and strong correlation to inflation and geopolitical risk make it a proven reserve asset.
- Bitcoin offers greater upside potential but carries higher volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and dependency on liquidity and sentiment.
- Diversification may be the most prudent approach, as each asset hedges different macro scenarios. Gold tends to shine in crisis, while Bitcoin thrives in liquidity-driven bull cycles.
- Key signals to monitor: inflation trends, central-bank gold purchases, Bitcoin adoption rates, and shifts in monetary policy.
Ultimately, both assets can serve as partial hedges, but not interchangeable ones. Their contrasting 2025 performance underscores the importance of understanding what drives each market rather than assuming both react identically to a weakening dollar.





Alphabet Shares Jump 8% as Revenue Surges Past $100 Billion
Alphabet’s stock climbed 8% after reporting record quarterly revenue of $102.3 billion, beating forecasts and raising its AI infrastructure budget to $92 billion for 2025.

Alphabet Inc. delivered a blowout third-quarter report, sending shares up 8% in premarket trading after the company smashed earnings and revenue expectations. The Google parent reported earnings per share of $2.87, easily topping Wall Street’s estimate of $2.26 and rising sharply from $2.12 a year earlier.
Revenue soared 16% year over year to $102.3 billion, marking the first time in company history that Alphabet crossed the $100 billion mark in a single quarter. Analysts called it a defining moment for the search and cloud giant, crediting strong performance across its core units – Google Search, YouTube, and Google Cloud.
AI and Cloud Lead the Growth Story
Alphabet’s results were driven by rapid expansion in Google Cloud, which posted a 34% jump in sales year over year. The unit’s operating margin rose to 24% from 17% a year ago, underscoring how scale and disciplined cost management are beginning to pay off.
The company also raised its 2025 AI data-center spending forecast to $92 billion, up from a prior estimate of $85 billion. Executives said the investment will help meet accelerating demand for AI infrastructure, reflecting the firm’s determination to stay ahead of competitors like Amazon and Microsoft in the race to power next-generation AI applications.
Profitability, Penalties, and Market Reaction
Alphabet’s operating margin came in at 30.5%, slightly below expectations and down from 32.3% last year, largely due to a $3.5 billion European Commission fine. Excluding that charge, margins would have reached 33.9%, signaling that profitability remains strong despite heavy AI spending.
Analysts largely dismissed the impact of the fine, noting that Alphabet’s diversified revenue base continues to deliver consistent growth. They pointed to expanding AI monetization in Search, resilient ad performance on YouTube, and cloud profitability as reasons for renewed investor confidence.
With shares up 8% following the report, market sentiment suggests investors are encouraged by Alphabet’s ability to grow aggressively while maintaining solid margins. Key metrics to watch include cloud-unit margins, ad revenue momentum, and the company’s execution of its expanded AI infrastructure strategy.
As previously covered, Alphabet’s transformation from a search-driven company into a global AI-cloud powerhouse is well underway – and this record-breaking quarter marks another milestone in that evolution.





JPMorgan Tokenizes Private Equity Fund on Proprietary Blockchain
JPMorgan has tokenized a private-equity fund using its in-house blockchain platform, opening the door for wealthy clients to access alternative investment strategies via digital tokens.

JPMorgan, the U.S. banking giant, has taken a significant step into the field of asset tokenization by launching a tokenized private-equity fund on its proprietary blockchain platform. The offering is initially available to high-net-worth clients of its private banking arm, and represents one of the most concrete moves by a major bank into real-world-asset digitization.
The firm’s internal platform, known as Kinexys Fund Flow, will support the new token offering and is scheduled for full deployment in 2026. The tokenized fund converts traditional ownership shares into blockchain tokens, allowing faster settlement, real-time ownership tracking and greater liquidity potential compared to legacy fund structures.
Inside JPMorgan’s Tokenization Strategy
JPMorgan’s initiative reflects the growing alignment between traditional finance and blockchain-based infrastructure. By tokenizing a private-equity fund, the bank is reducing friction in capital-calls, settlement processes and ownership reporting – areas long viewed as inefficiencies in alternative investments. The move positions JPMorgan as a pioneer in bridging private markets with digital technology.
Tokenization could also broaden access: historically, private-equity and real-estate funds demanded large minimum commitments and lengthy lock-ups. By issuing tokens that represent ownership stakes, JPMorgan is laying groundwork for fractionalised access, secondary-market trading and potential collateral usage – all of which may open alternatives to a wider range of investors over time.
Future Adoption and Industry Implications
For investors and asset managers, the development sends a clear signal that alternative investments are going digital. The key questions now include how quickly the tokenized fund gains scale, how liquidity develops, and whether regulatory frameworks keep pace. Metrics to watch include the number of token holdings, turnover in tokenised shares and whether other asset classes – real estate, private credit, hedge funds – are added to the platform.
On the flip side, risks reside in execution: blockchain infrastructure must be secure and compliant, and client-adoption may take time. Regulation remains a wildcard, especially in how tokens are classified, taxed and traded. In addition, token value may depend on the underlying fund performance, not simply on the novelty of digital issuance.
As previously covered, the tokenization of real-world assets is moving from concept to live implementation – JPMorgan’s move could accelerate the trend in institutional investing.




